In the field of electric vehicles, there are high technical requirements for the casting process of aluminum alloy motor housings to achieve lightweight, robust, durable, and economically feasible solutions. Today, let's discuss the manufacturing process and development trends of motor housings.
Integration trend in motor housing design
Amid increasingly stringent requirements on CO2 emissions and fuel consumption, the development of new energy vehicles has also driven advances in drivetrains. From hybrid to plug-in hybrid and pure electric vehicles, various types of drive motors have emerged. Early hybrid vehicles were retrofitted from gasoline cars, with drive motors consisting of multiple components and low integration. With advancements in motor technology, there is a preference for drive motors with simpler structures, fewer components, and higher integration. For instance, as shown in Figure 1 of the BMW i3 motor structure, it mainly comprises an external housing, stator frame, transmission flange, and housing for electronic components, mostly made of aluminum die-castings. To actively cool the motor, the housing incorporates internal liquid cooling channels. This design offers flexibility in design and is suitable for mold casting, particularly advantageous for small motors.

As new electric vehicle platforms continue to emerge and the need for mass production increases, there is a sharp rise in requirements for lightweight motors, compact installation space, high power-to-weight ratios, efficiency, and overall cost-effectiveness, thereby driving changes in motor architecture. Hence, integrated motor design has become a focal point. This means motors consist of only a few components such as housing, gearbox, and power electronics, all individually cast and assembled using various technologies before integration into the motor housing. Integrated design solutions also offer manufacturing advantages by eliminating critical interfaces, thereby reducing manufacturing costs, while also achieving weight reduction and performance enhancement.

Water-cooled cavity design of motor housings
The design of motor housings and cooling channels is crucial for motor operation, with optimized channel designs enhancing cost-effectiveness, typically achieved through simulation analysis.
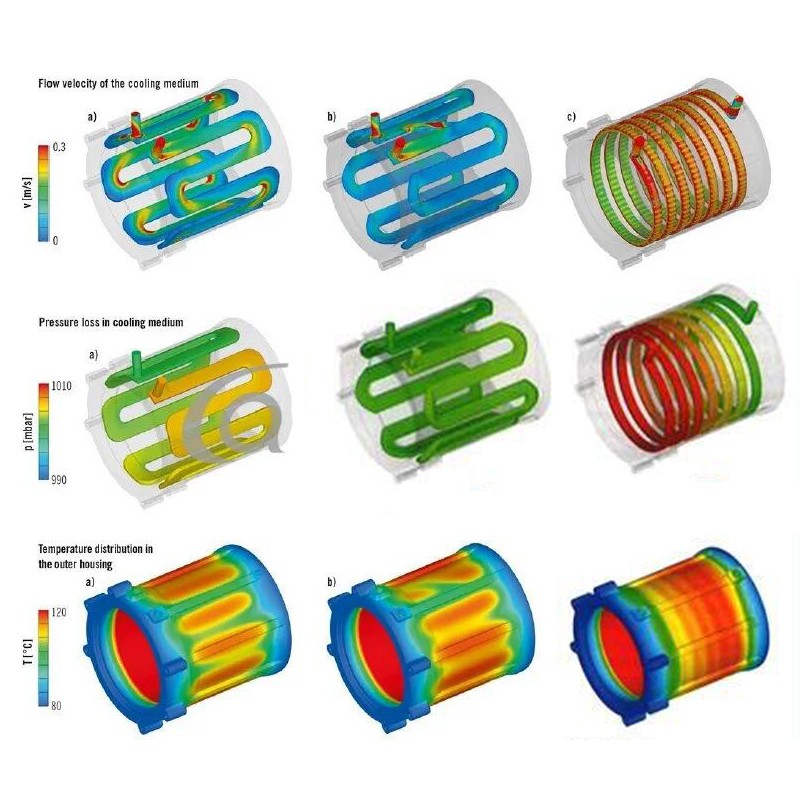
Cooling channel structures are generally designed in serpentines or spirals, as seen from Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation results. Figure a shows the initial curved design of a cooling channel, while variant b features lower flow resistance achieved by inserting support ribs to enhance sand core rigidity. Flow calculations demonstrate that channel efficiency is unaffected by design. Variant c calculates results for a spiral cooling channel, offering a larger cooling surface area and increased turbulence of the cooling medium, thereby improving heat transfer. Spiral-type cooling channels are currently one of the most common solutions in electric motor housing cooling design.
Material and processing technology of motor housings
Motor housing materials require the selection of suitable cast aluminum alloys and heat treatment processes to meet usage demands. The choice of casting process also affects the quality and mechanical properties of castings. Factors considered during material selection include:
- Pressing the stator into the inner housing and bearing loads during operation → alloys with high strength and elongation
- Dimensional stability during use → appropriate selection of heat-treated casting materials
- Preventing surface corrosion, especially on external sealing surfaces of the housing → use of corrosion-resistant alloys
- Shielding electromagnetic fields → ensuring electromagnetic compatibility of materials used.
During motor housing development, consideration must not only be given to whether materials meet the above performance requirements but also to the comprehensive consideration of process selection and production processing costs. The main forms of motor housing processing technology are die-casting and extruded profiles, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Profile motor housings offer stable performance and affordable costs but are only suitable for small-caliber motor housings with structurally simple functions. Die-cast motor housings have a wide range of applications, capable of meeting the needs of large-caliber motor housings and complex integrated motor housings, making it the mainstream processing technology in the market.