Lasers are used extensively in various fields due to their exceptional performance advantages. They are applied in industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, precision measurement and detection, communications and information processing, medical applications, and military uses, with notable results. Lasers can concentrate extremely high energy to process different materials, allowing for tasks like drilling hundreds of holes in a needle. In biological systems, lasers can induce stimulation, mutation, burning, or vaporization, making them useful in medical and agricultural applications. In communications, a fiber optic cable carrying signals via laser can transmit information equivalent to that of 20,000 telephone copper lines. In the military, lasers are used for communication, night vision, early warning, and ranging, as well as in various laser weapons and guided laser weapons that have already been put into practical use.
The market for lasers is vast, and their applications will become even more widespread in the future. Lasers are high-tech electronic products with high integration, and therefore, they are expensive. Below, the thermal management expert from Lorithermal introduces the technology of laser cooling.
A laser’s heat sources generally include three aspects. For example, in a fiber laser, the heat sources include: high-power power supply heat; LD array heat (with a slope efficiency of 50%); heat absorbed by the double-clad fiber material; and quantum deficit heat. The cooling design must address the characteristics of these heat sources and be tailored to the cooling needs of each component, eventually forming a complete laser cooling system. Laser cooling designs generally involve four approaches: natural cooling, air cooling, water cooling, and phase-change cooling technologies.
Natural Cooling Technology: This involves adding a natural cooling heat sink to the heat source, which transfers the heat away from the source and then dissipates it into the air naturally. Natural cooling is suitable for low-power lasers where the heat generation is minimal, and natural cooling heat sinks can meet the cooling requirements.
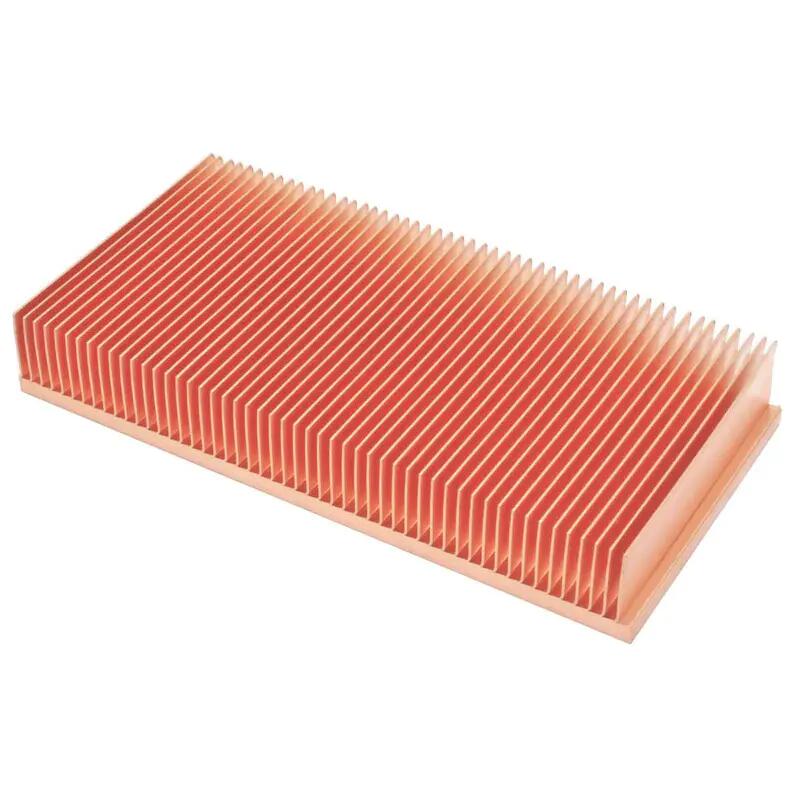
Air Cooling Technology: Air cooling builds on natural cooling by adding a fan to enhance air circulation, thereby dissipating the heat from the heat sink more effectively. Air coolers are typically designed with a base plate and fins; the base plate is in direct contact with the heat source, while the fins are placed close to the fan.
Water Cooling Technology: Water cooling provides effective cooling without the vibrations associated with other methods, making it widely used in high-power lasers. The downside is that it adds weight and volume to the laser system. A custom water cooling plate is installed on the heat source, connecting to an external water cooling system, creating a circulation system.
Phase-Change Cooling Technology: Phase-change cooling is an extension of natural cooling. It involves adding copper or aluminum heat sinks to the heat source and equipping them with heat pipes that have phase-change thermal conductivity. These heat pipes connect to the housing or external heat sink, efficiently directing and transferring internal heat to the laser's exterior for cooling.
Different types of lasers and power levels require different cooling methods. The cooling system needs to be designed according to specific requirements, and the designed cooler must be tested through thermal simulation and prototyping to ensure it meets the cooling requirements.
Lori is a professional heat sink manufacturer offering customized services. We can design and produce the most suitable cooling solutions for your semiconductor lasers. If needed, please contact us!