There are various forming and processing techniques for aluminum alloy heat sinks, each with its unique characteristics and applicable scenarios.
Integrated Forming
An integrated forming heat sink has its cooling fins and base plate as a single unit, eliminating thermal contact resistance.
Die-Cast Aluminum Heat Sink
The advantages of die-cast aluminum heat sinks include low cost, high production efficiency, and the ability to create complex shapes. However, the material used is usually die-cast aluminum, which has a relatively low thermal conductivity, and there are limitations on the size of the fine cooling fins. Additionally, die-casting is suitable for high-volume production to spread out the cost of molds.
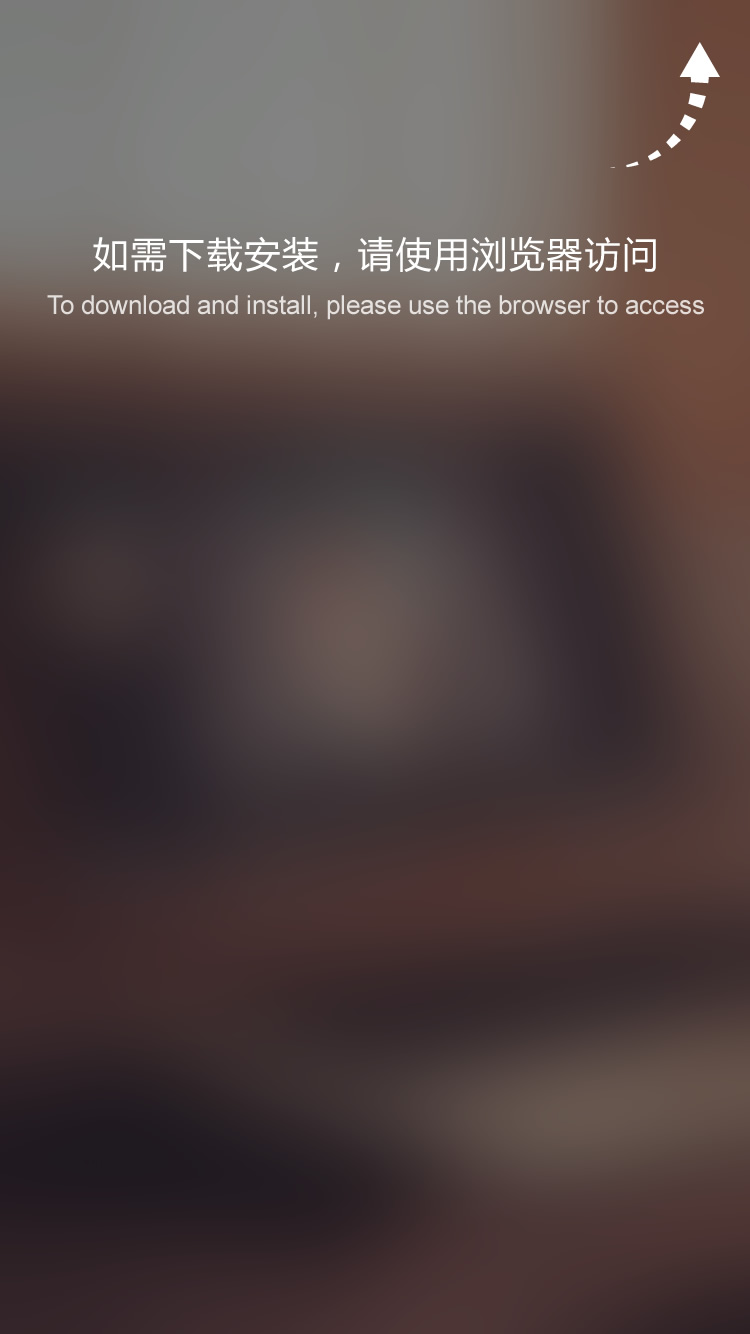
Extruded Aluminum Heat Sink
The advantages of extruded aluminum heat sinks are low cost, short development cycle, and relatively high thermal conductivity of the material. Fine cooling fins can be made, but the ratio of fin height to thickness is limited (generally not exceeding 20), and complex shapes cannot be achieved.
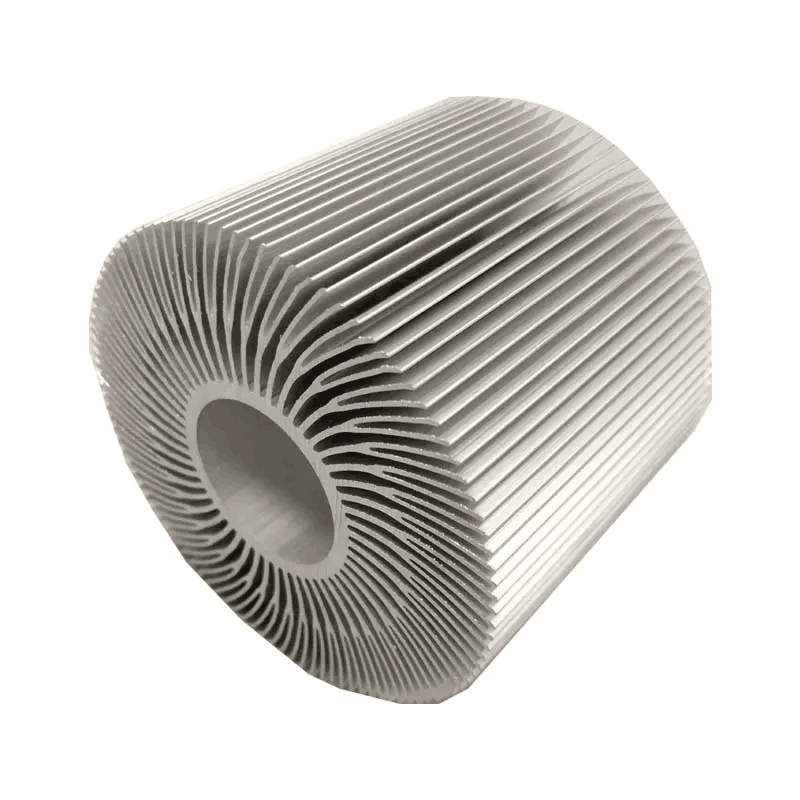
Cold forged Heat Sink
The advantages of cold-stamped heat sinks include the ability to create fine cooling fins and relatively high thermal conductivity of the material. However, the cost is relatively high, and the ability to handle irregular shapes is better than that of extruded aluminum.
There is also a special type of integrated forming heat sink, as shown in the figure below:
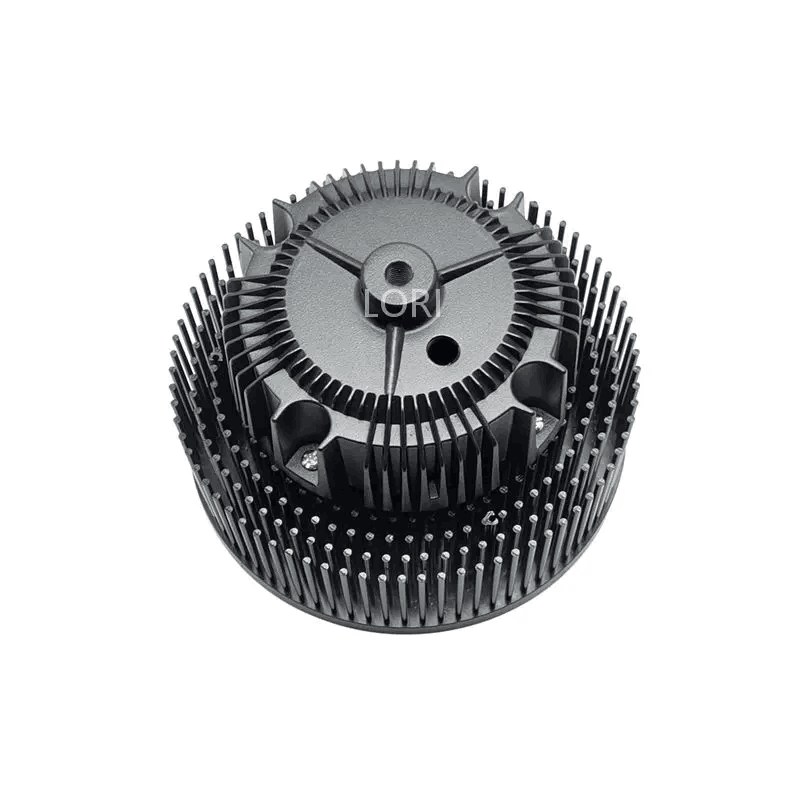

Skiving fin Heat Sink
Skiving fin heat sinks can be made from copper, which has high thermal conductivity. The fins can be very fine, as they are directly chiseled from the base plate. However, when the fins are tall and long, they are susceptible to deformation due to stress.
High-density fins can also be made inside water cooling heads using chiseling. We will discuss this in a separate topic later, so we won't elaborate here.
It can be seen that the thickness, spacing, and height of the fins in integrated forming heat sinks are limited, which means that in some projects, they cannot meet the cooling requirements. This has led to the development of non-integrated forming heat sinks.

Non-Integrated Forming
Non-integrated forming heat sinks have the cooling fins and base plate processed separately and then assembled using welding, adhesive, or interference fitting techniques, resulting in thermal contact resistance.
Folded Fin Heat Sink
Folded fin heat sinks can be made from copper or aluminum, with high thermal conductivity. The fins can be very fine. Fins are first processed and then folded into the desired shape and welded to the base plate. This method is costly.
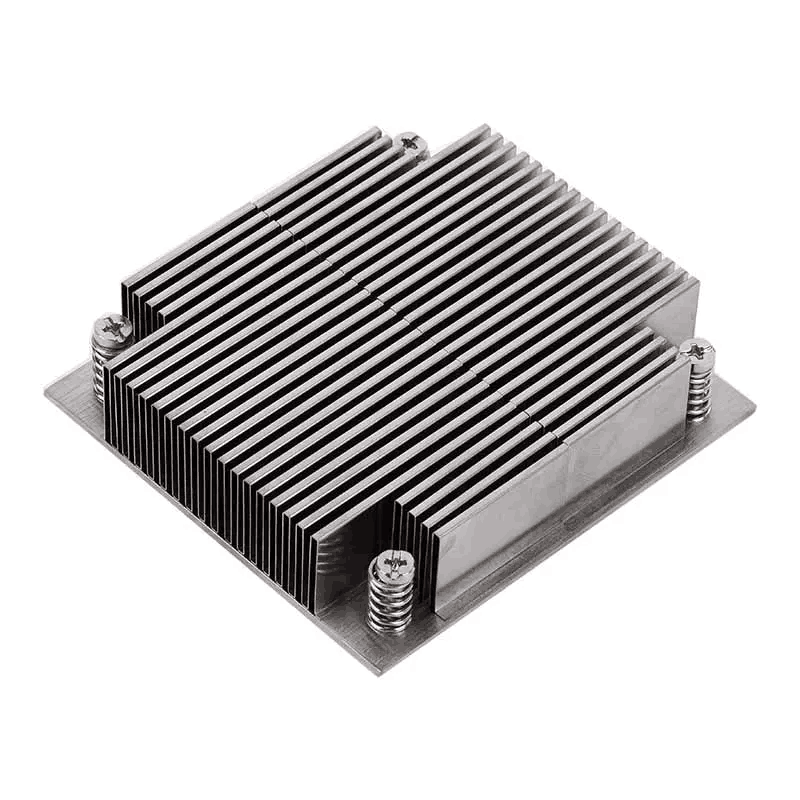
Stamped Fin Heat Sink
Stamped fin heat sinks can be made from copper or aluminum with high thermal conductivity and can be very fine. The fins are first processed and then notched to fit and welded to the base plate. The process is complex and the cost is high.
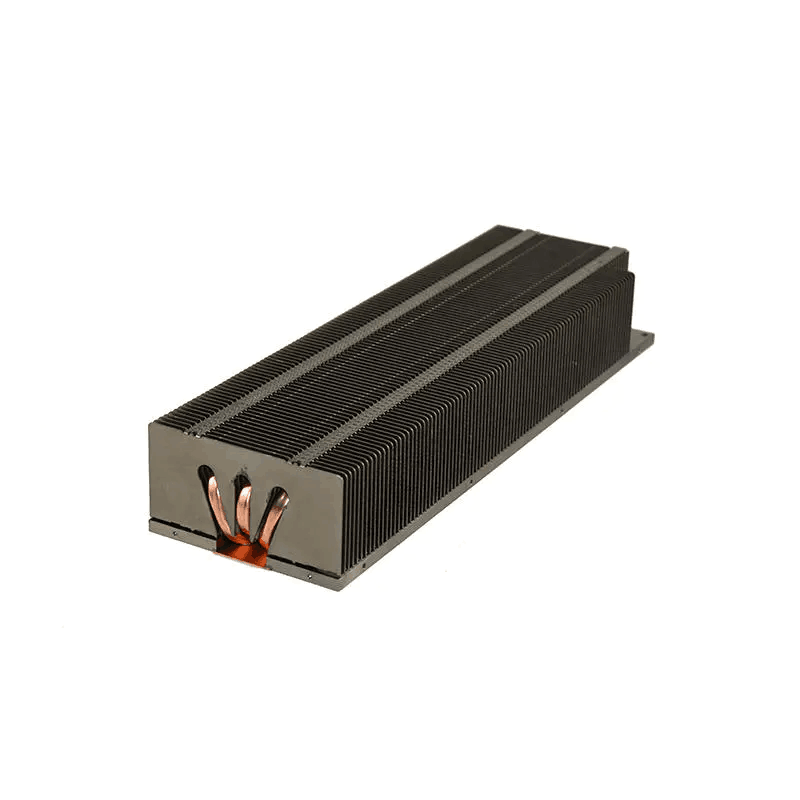

Inserted-Fin Heat Sink
Inserted-fin heat sinks have flexible thermal conductivity, fin thickness, and spacing compared to die-casting. The fins are inserted into the base plate, but the manufacturing difficulty is high, with a lower yield rate and relatively higher cost.
Comparison of Heat Sink Processing Techniques
Process | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Extruded | Best cost-performance ratio, high thermal conductivity | Cannot achieve complex shapes, requires extensive machining |
Die-Casting | Versatile shapes, attractive designs | High mold costs, cost-effective only for large volumes, low thermal conductivity, limited effectiveness |
| Skiving fin | Can achieve the highest density and maximize fin area | Cannot achieve complex shapes, height is limited |
| Stamped Fin | High fin density and height | High cost, high mold costs, suitable for mass production, high requirements for the joining area |
| Inserted-Fin | High fin count ratio, large surface area | Special process, generally used for specific products, relatively expensive |