A server is defined as a computer that runs management software in a local area network to control access to the network or network resources, providing resources to other computers on the network so that they can operate like workstations and offer services to users. Servers can be categorized into types such as file servers, database servers, and application servers, each providing different services to meet various application needs.
Server configurations typically include key components such as CPU, memory (RAM), storage devices, motherboard, power supply, and cooling systems. Servers usually have CPUs with more cores and higher processing power, large memory capacity to support concurrent handling of numerous requests, and storage devices including hard disk drives and solid-state drives, often utilizing RAID configurations to ensure data integrity. The motherboard is designed with enhanced data transfer capabilities and additional expansion slots. Power supplies are usually designed with redundancy and hot-swappable features, while cooling systems are crucial to prevent hardware overheating. The main cooling methods for servers include:
1. Fan Cooling
Fans generate airflow to expel hot air from inside the server and introduce cool air. The primary working principle of cooling fans is to drive the fan blades to rotate, creating airflow that accelerates the evaporation of cooling fluids, thereby carrying away the heat generated inside the server. Fans produce airflow that helps the cooling fluid evaporate more quickly. The evaporation process absorbs the server's internal heat, which is then carried away by the heat sink and expelled outside the server by the fan.
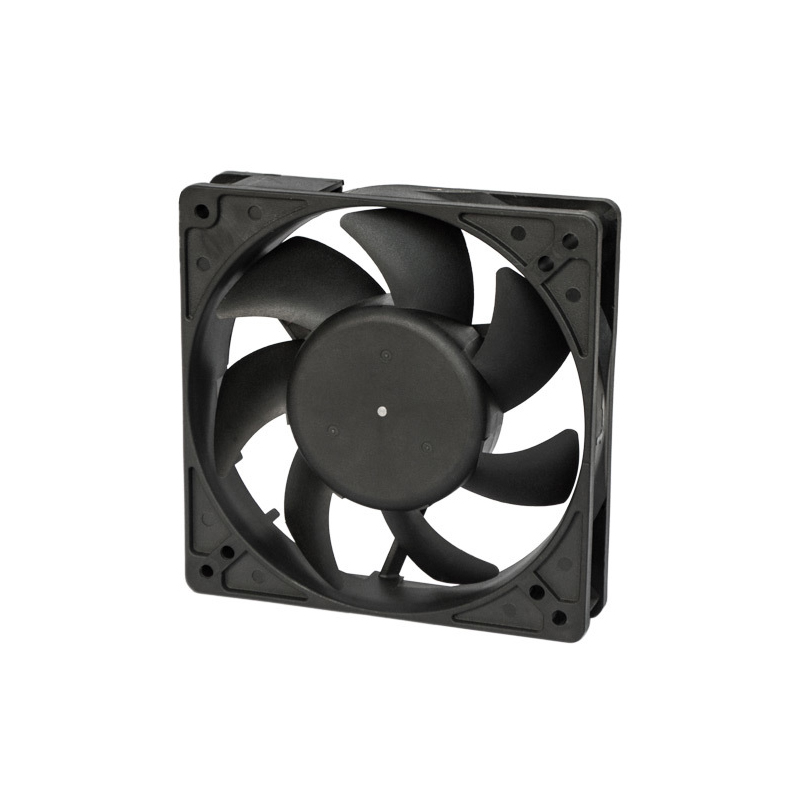

2. Heat Sinks
Heat sinks are installed on heat-generating components of the server to dissipate heat through contact with the air. Heat sinks are crucial components of the server cooling system, designed to conduct and release the heat generated inside the server to maintain optimal operating temperatures and ensure performance and stability. Heat sinks are typically made from materials with good thermal conductivity, such as aluminum alloys, copper, or copper-aluminum composites, to enhance cooling efficiency.
The main role of a heat sink is to transfer heat from the server's internal components to the heat sink surface, increasing the heat dissipation area and transferring the heat away through cooling components such as fans, thereby reducing the server's temperature. Effective heat dissipation helps prevent overheating, avoiding performance degradation and hardware damage.
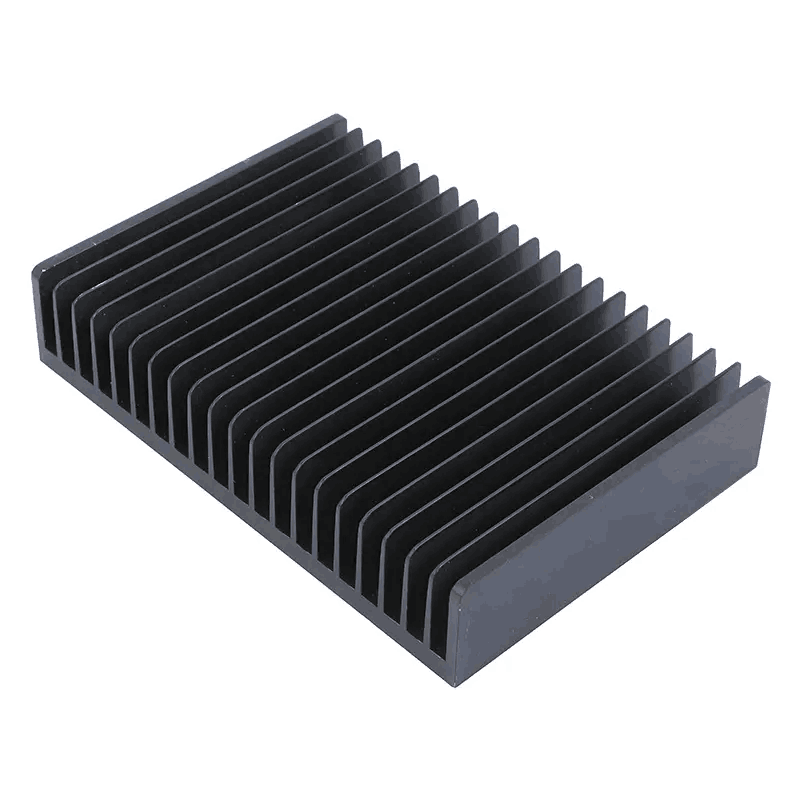
3. Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling uses fluids (usually water) as the cooling medium to carry away heat through circulation. Liquid cooling is an advanced cooling technology increasingly used in data centers and server cooling. Liquid cooling technology is typically divided into two types: cold plate and immersion cooling. Cold plate liquid cooling involves indirect contact between the liquid and the server's heat-generating components, transferring heat via thermal conduction. Immersion cooling involves completely immersing server components in a cooling liquid, utilizing phase change of the liquid to absorb and release heat.
Cold plate liquid cooling generally involves one or more cooling fluids that flow through cooling plates inside the server, making contact with heat-generating components to carry away heat, which is then released through cooling towers or condensers. This method can effectively improve cooling efficiency and lower server operating temperatures, with the liquid not making direct contact with electronic components.
Immersion cooling is more efficient, completely immersing the server's motherboard, CPU, memory, and other high-heat components in a coolant. During operation, heat generated by the components raises the coolant temperature, causing the coolant to change phase from liquid to gas, absorbing heat through vaporization and transferring it away.
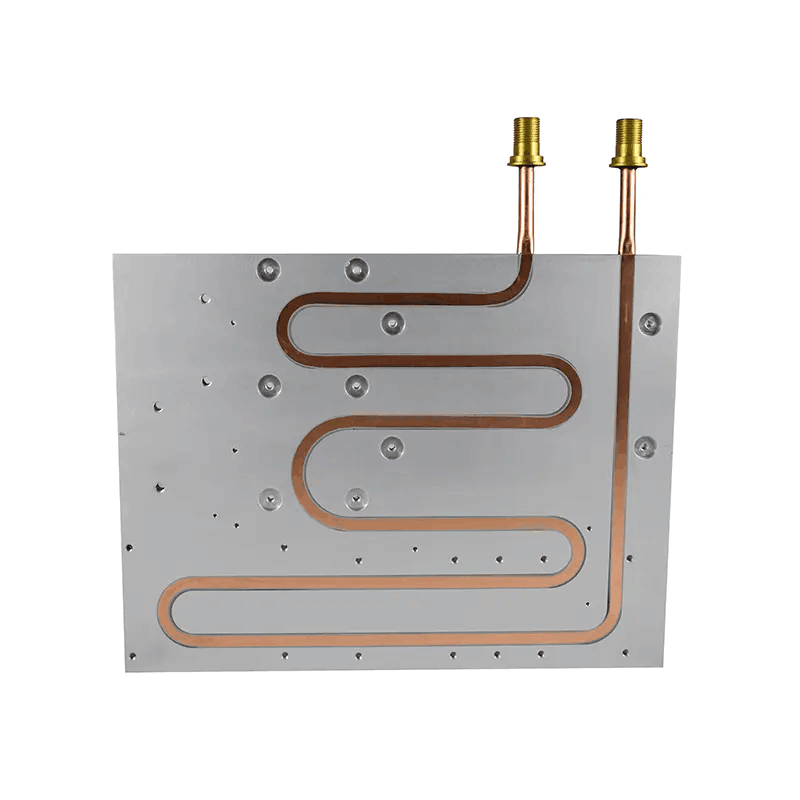
4. Phase Change Cooling
Phase change cooling utilizes the heat absorption properties of materials undergoing phase changes. Specifically, phase change cooling typically involves evaporation and condensation processes. Inside the server, heat is transferred to the evaporator, causing phase change materials to convert into gas, which is then condensed back into liquid by the condenser, releasing heat.
The advantages of phase change coolers include rapid cooling, efficiency, reliability, and noiseless operation. Compared to traditional cooling methods, phase change cooling provides higher cooling capacity, lowering server temperatures. Phase change coolers are widely used in electronics, optoelectronics, and thermoelectronics, especially in CPU and GPU applications, offering excellent cooling solutions that significantly improve system stability and reliability. However, phase change coolers are relatively expensive, heavy, and require precise control of phase change materials' temperature and heat. Additionally, phase change cooling systems are complex and require specialized equipment and technical support.
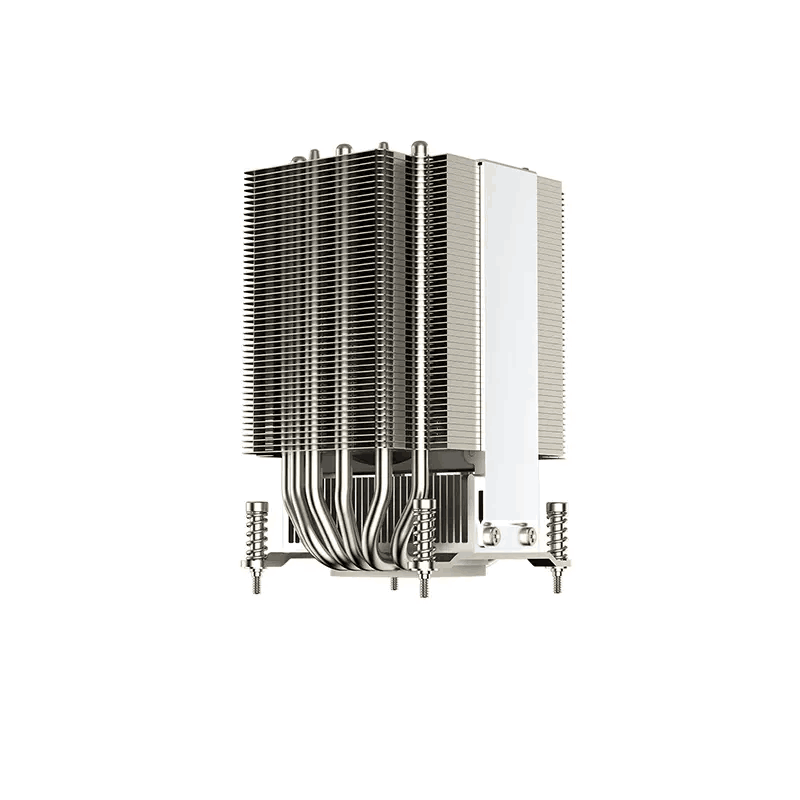
5. Heat Pipe Cooling
Heat pipe cooling transfers heat from the heat source to the heat sink through heat pipes. Heat pipe cooling, also known as thermal pipe cooling, is an efficient and reliable cooling technology. It uses the principle of heat pipes to transfer heat rapidly from the heat source to the heat sink through the evaporation and condensation of working fluids.
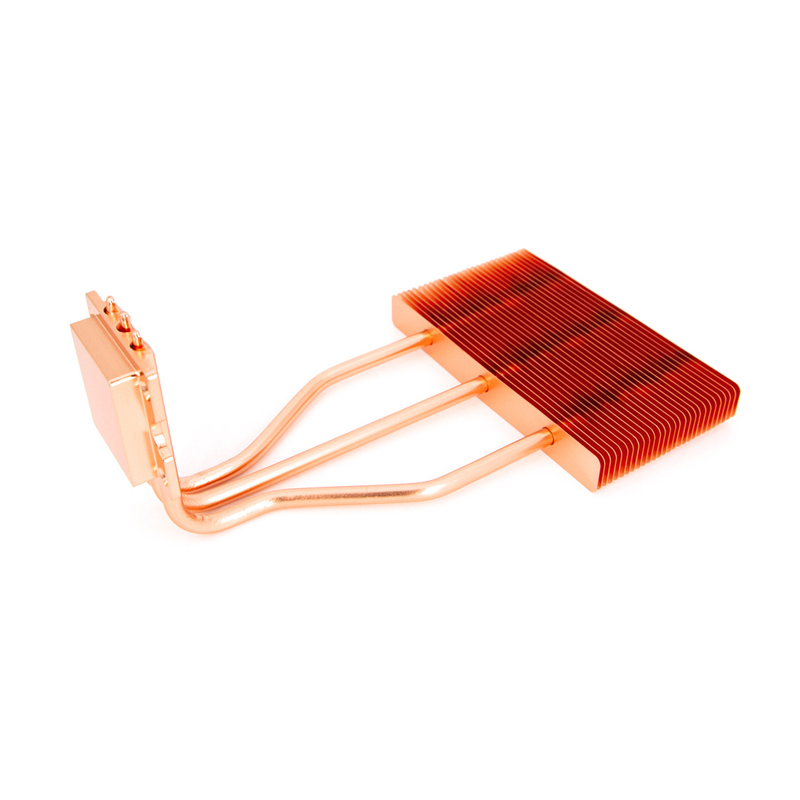
In a heat pipe cooling system, heat pipes are typically installed inside the server, with one end in contact with the CPU, GPU, or other heat sources and the other end connected to a heat sink. When the heat source generates heat, the liquid in the heat pipe's evaporator end quickly evaporates into vapor, which flows to the condenser end, releases heat, and condenses back into liquid. The liquid then flows back to the evaporator end through the heat pipe's capillary structure, forming a continuous cycle. The advantages of heat pipe cooling include high efficiency, relying on capillary action and vapor pressure differences without external power, making it more energy-efficient and reliable. It also has a compact structure, making it suitable for high-density server environments, and offers good thermal balance, ensuring a small temperature gradient between the heat source and the heat sink for more uniform heat distribution.
6. Environmental Control
Environmental control involves regulating the temperature and humidity of the server room through air conditioning systems and other means. Environmental control is crucial for ensuring the efficient and stable operation of servers. It includes temperature, humidity, airflow, and dust control within the server room or placement area.
Temperature Control: Servers need to operate at suitable temperatures to avoid performance degradation or hardware damage due to overheating. Typically, the server room temperature should be controlled between 20°C and 25°C. To achieve this, efficient air conditioning systems are required, and the air conditioning mode should be adjusted based on the actual conditions of the server room.
Humidity Control: Proper humidity helps prevent static electricity and reduce equipment failure rates. The server room humidity should generally be maintained between 40% and 60% RH. Humidity can be adjusted using humidity sensors and dehumidifiers or humidifiers.
Airflow: Proper airflow helps lower server temperatures and improves cooling efficiency. The server room should be equipped with adequate ventilation equipment, such as fans and air conditioners, to ensure smooth airflow. Additionally, servers should not be arranged too densely to allow unobstructed air circulation.
Dust Control: Dust accumulation can affect cooling efficiency and lead to hardware failures. Therefore, server rooms should be regularly cleaned to minimize dust buildup. Additionally, dust control measures, such as installing dust filters or curtains at the room entrance, can help reduce the amount of dust entering the server room.