The terms “heat sink” and “heat exchanger” often come up when talking about thermal management in electronics, data centers, and various industries. But are heat sinks and heat exchangers the same thing? Both components help regulate temperature and transfer heat, but a heat exchanger is not necessarily a heat sink. There is some difference in them.
What is a heat sink?
A heat sink is a passive heat exchanger used to absorb and dissipate heat from sensitive electronic components or machinery such as cpu, gpu, power electronics and LED lights. Its main function is to prevent overheating and maintain optimal operating temperatures for these components.
Heat sinks usually consist of metal, aluminum or copper, because they have good thermal conductivity. They usually have an increased surface area through fins to maximize heat dissipation. When heat is generated by a component, the heat sink draws it away and radiates it to the surrounding air or cooling medium.
The main characteristics of a heat exchanger:
◪Passive cooling solution (no moving parts);
◪Primarily used for localized thermal management;
◪Dissipates heat primarily to the air or surroundings;
◪Commonly used in consumer electronics and small system.
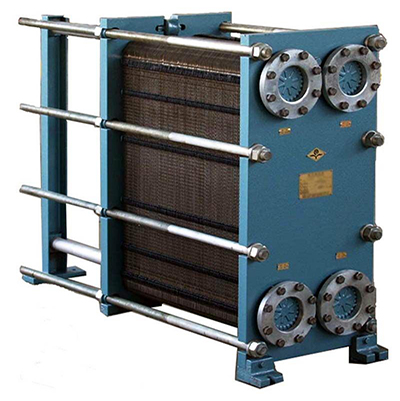
What is a heat exchanger?
A heat exchanger, on the other hand, is a device that transfers heat between two or more fluids without allowing them to mix. Heat exchangers are usually made with a medium such as air, water or oil and are used to absorb heat from one system and then release it into another.
Unlike heat sinks, heat exchangers are designed for heat transfer on a larger scale and typically operate in systems that transfer heat through different fluid paths. For example, in a data center, a heat exchanger may be used in a fluid cooling system where a coolant absorbs heat from a processor and then transfers it to a heat exchanger, which releases the heat to another fluid or to the atmosphere. A typical example of a heat exchanger is the internal combustion engine. It is mainly categorized into double tube heat exchangers, shell and tube heat exchangers, and plate heat exchangers; another typical example is the heat sink.
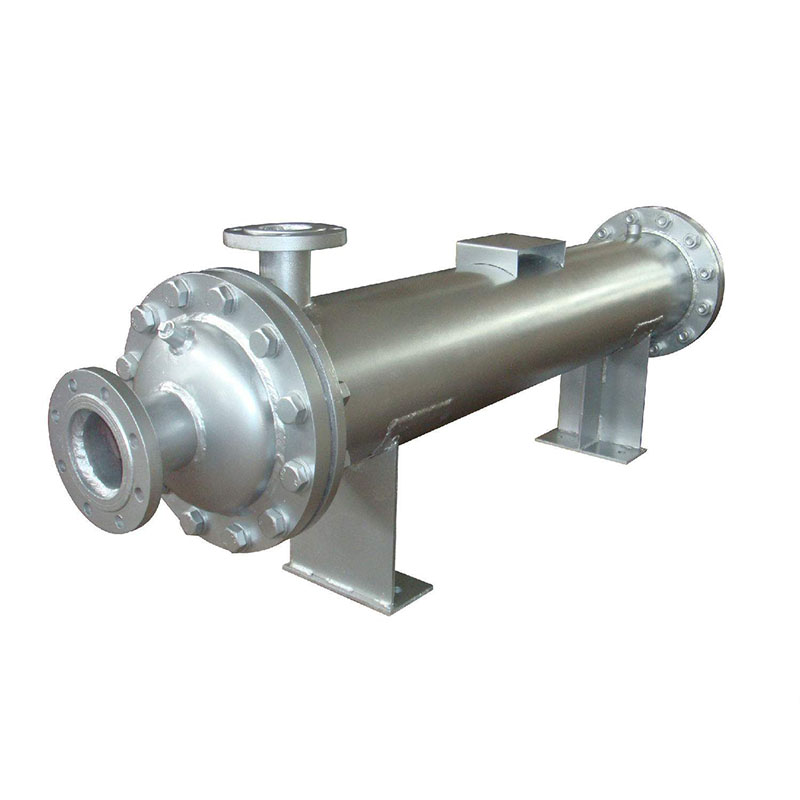

shell and tube heat exchanger
The main characteristics of a heat exchanger:
◪Transfer heat between different fluids;
◪Can be passive or active (depending on the design);
◪Typically used for fluid cooling in larger systems such as HVAC, industrial applications or data centers;
◪Can withstand higher heat loads than heat sinks.
Differences between heat sinks and heat exchangers
While heat sinks and heat exchangers both have the same goal - to manage heat - they work differently and apply fluids differently.
Functional difference: A heat sink primarily distributes heat to the surrounding air. It is ideal for localized cooling of individual components.
A heat exchanger transfers heat from one fluid to another, usually on a larger scale. It is used in systems that need to transfer heat from critical components such as processors or machinery.
Size and scale difference: Heat sinks are usually smaller and are used for individual components such as cpu's, graphics cards or power supplies. Heat exchangers are larger and are designed to cool entire systems or transfer heat across fluids in large-scale applications such as industrial systems or data centers.
Heat Transfer Media: Heat sinks transfer heat to air or other surrounding materials by conduction and convection. Heat exchangers work by transferring heat between two different fluids, such as air-to-liquid or liquid-to-liquid.
Design Complexity Difference: heat sinks are usually simpler and are passive cooling with no moving parts. Heat exchangers can involve complex fluid dynamics and can include both passive and active components, such as pumps or fans.
In short, while a heat sink is a type of heat exchanger, a heat exchanger is not a heat sink; they are not the same thing. Heat sinks are designed for passive cooling on a smaller scale and are well suited for individual electronic components. Heat exchangers, however, are more complex devices used to manage the transfer of heat between fluids and are typically used in large-scale applications such as industrial systems or liquid cooling units in data centers.
Understanding the differences between these two thermal management systems is critical when choosing the right solution for your cooling needs. Whether you are designing a computer system, an industrial machine or a high-performance data center, choosing the right thermal technology can make all the difference in terms of performance and longevity.